Resetting MySQL root password
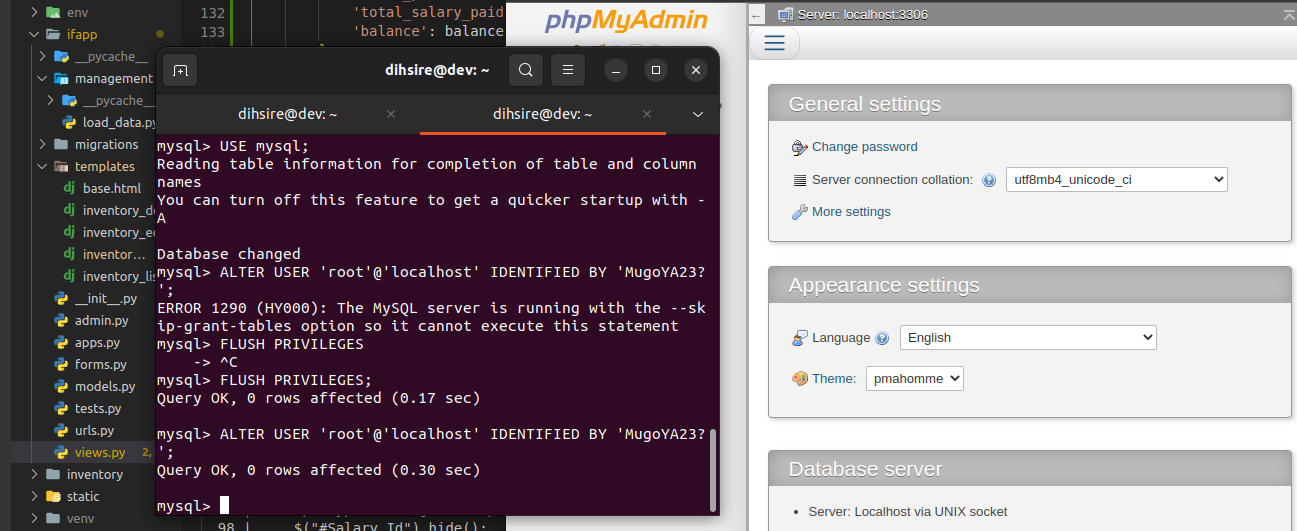
First Stop mysql using your teminal
sudo /etc/init.d/mysql stop
To resolve this issue, you can follow these steps:
-
Create the directory for the MySQL UNIX socket file:
sudo mkdir -p /var/run/mysqld -
Change the ownership of the directory to the MySQL user:
sudo chown mysql:mysql /var/run/mysqld -
Start the MySQL service with the
--skip-grant-tablesand--skip-networkingoptions:sudo mysqld_safe --skip-grant-tables --skip-networking &This command should start the MySQL service without performing any privilege checks and without enabling network connections.
Once the MySQL service is running, you can proceed with resetting the root password or performing any necessary recovery steps.
-
Stop the MySQL server:
sudo service mysql stop -
Start the MySQL server with the
--skip-grant-tablesoption:sudo mysqld_safe --skip-grant-tables & -
Open a new terminal window and log in to the MySQL server as the root user:
mysql -u root -
In the MySQL prompt, switch to the MySQL database:
USE mysql; -
Reset the root password:
UPDATE user SET authentication_string=PASSWORD('new_password') WHERE User='root';Replace
'new_password'with your desired password. -
Flush the privileges to apply the changes:
FLUSH PRIVILEGES; -
Repeat step 5 after flushing the pivileges -
Exit the MySQL prompt:
EXIT; -
Stop the running MySQL server:
sudo service mysql stop -
Start the MySQL server again:
sudo service mysql start
After following these steps, your root password should be reset to the new password you specified. Make sure to replace 'new_password' with your desired password in step 5.
June 1, 2023, 6:34 p.m. | Authored by Mugoya Dihfahsih
create username To join the discussion